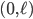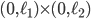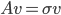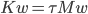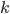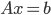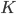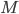Most literature about garbage collection contains a list of advantages of garbage collection. The lists of advantages known to me omit one advantage: certain concurrent algorithms require garbage collection.
I will demonstrate this point with an example in the programming language C, specifically the revision C11. Consider a singly-linked list where the pointer to the head of the list is concurrently read and written by multiple threads:
struct node
{
size_t value;
struct node* p_next;
};
typedef struct node node;
_Atomic(node*) p_head = ATOMIC_VAR_INIT(NULL);
The singly-linked list is considered empty if p_head is a null pointer. The thread T1 is only reading the list:
void* T1(void* args)
{
node* p = atomic_load(&p_head);
// more computations
// stop referencing the head of the list
return NULL;
}
The thread T2 removes the first element of the singly-linked list by trying to overwrite the pointer stored in p_head:
void* T2(void* args)
{
node* p = NULL;
node* p_next = NULL;
node* p_expected = NULL;
do
{
p = atomic_load(&p_head);
if( !p )
break;
p_next = p->p_next;
p_expected = p;
} while(!atomic_compare_exchange_strong(&p_head, &p_expected, p_next));
// ensure other threads stopped referencing p
free(p);
return NULL;
}
T2 relies on compare-and-swap in line 16 to detect interference of other threads.
After successfully updating p_head, the memory referenced by p needs to be freed after all threads stopped referencing this memory and in general, this requires a garbage collector. Waiting does not help because the threads holding references might have been stopped by the operating system. Scanning the stack, the heap, and the other threads' CPU registers is not possible in many languages or not covered by the programming language standard and besides, such a scan is an integral part of any tracing garbage collector.
In the introduction I wrote that certain concurrent algorithms require garbage collection and more accurately, it should say: In the absence of special guarantees, certain concurrent algorithms require garbage collection. For example, if we can guarantee that threads hold their references to the singly-linked list only for a certain amount of time, then there is no need for garbage collection and this fact is used in the Linux kernel when using the read-copy-update mechanisms.